Table of Contents
Learning Through Play is one of the most effective approaches in childhood education, backed by global research and classroom evidence. As of 2026-01-22, neuroscience confirms that 90% of brain development occurs before age 5, underscoring the critical role of early learning experiences. Play-based learning supports cognitive growth, language development, emotional regulation, and social skills during this window. We see stronger outcomes when children actively explore, rather than passively receive information.
UNICEF reports that play-based environments improve school readiness, problem-solving ability, and attention span across diverse socioeconomic settings. Learning Through Play works because it aligns with how young brains develop. Children learn best when they are curious, engaged, and emotionally safe. Play provides that structure naturally and consistently.
In early education settings across the United States, play-centered classrooms show higher engagement and better long-term learning retention. Harvard Graduate School of Education highlights that guided Play produces stronger academic outcomes than direct instruction alone.
This article explains seven proven methods of Learning Through Play, grounded in current data and expert insight. Each method includes context, practical application, and a clear takeaway for parents and educators focused on early learning success.
Why Learning Through Play Works in Early Childhood
Brain Development and Play-Based Learning
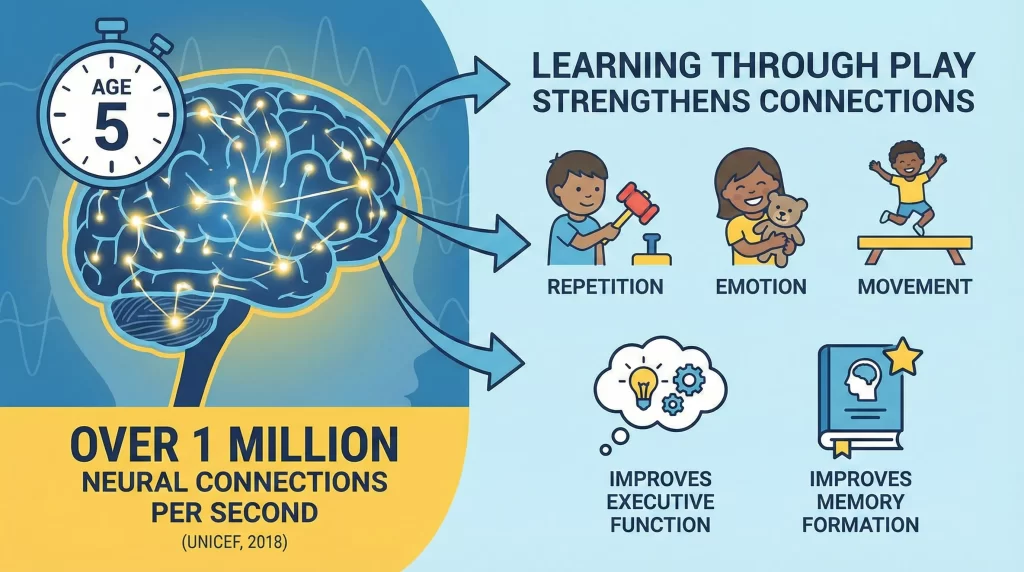
Early childhood is a period of rapid neural growth. By age 5, children form over 1 million neural connections per second, according to UNICEF research published in 2018. Learning Through Play strengthens these connections through repetition, emotion, and movement. Play activates multiple brain regions at once, improving memory formation and executive function.
When children play, they practice decision-making, language use, and emotional control simultaneously. This integrated learning improves outcomes compared to rote instruction. A 2023 Harvard study found that guided Play improves vocabulary acquisition by 23% compared to traditional teaching methods. Play-based learning builds strong cognitive foundations that support later academic success.
7 Fun Methods to Boost Early Learning Through Play
1. Guided Pretend Play
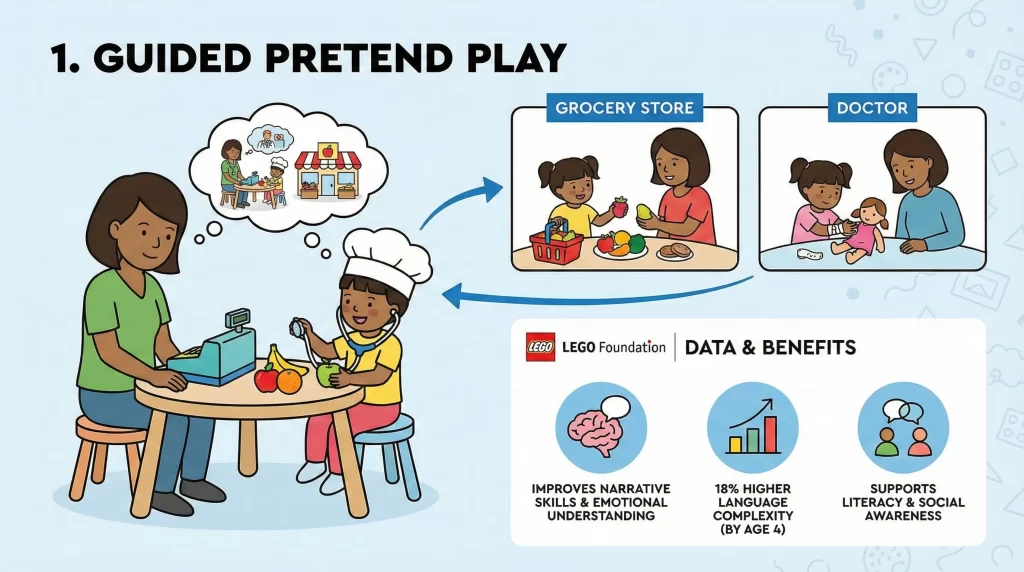
Guided pretend Play combines imagination with adult support. Teachers or parents introduce themes while allowing children to lead interactions. Examples include playing grocery store or doctor.
Data from the LEGO Foundation shows that guided pretend Play improves narrative skills and emotional understanding. Children practicing role-play demonstrate 18% higher language complexity by age 4. This method supports literacy and social awareness through structured imagination.
2. Learning Games With Rules
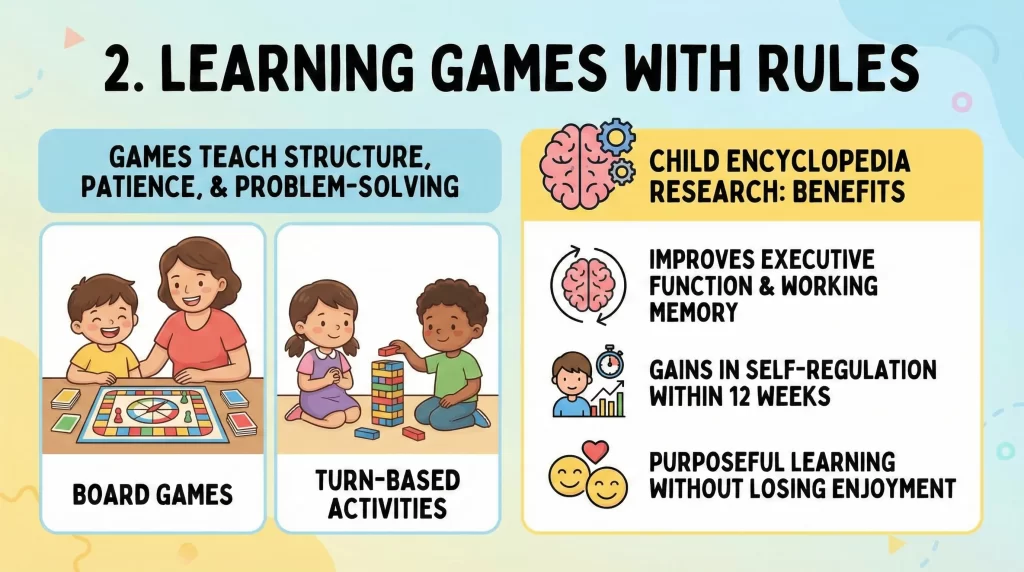
Games with simple rules teach children structure, patience, and problem-solving. Board games and turn-based activities are effective examples.
Research from the Child Encyclopedia confirms that rule-based Play improves executive function and working memory. Children engaged in these games show measurable gains in self-regulation within 12 weeks. Learning Through Play becomes purposeful without losing enjoyment.
3. Sensory Play Activities
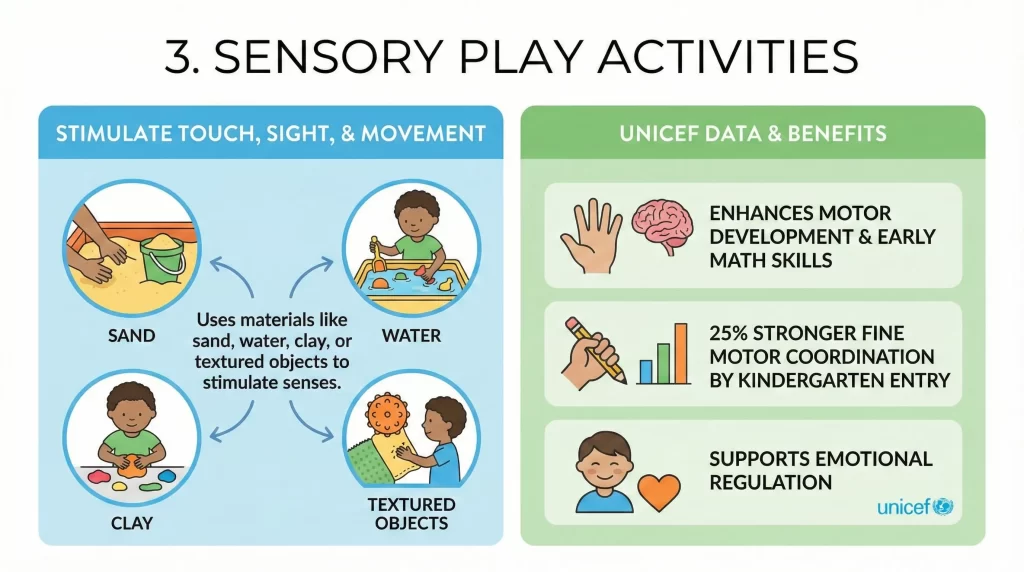
Sensory Play uses materials like sand, water, clay, or textured objects. These activities stimulate touch, sight, and movement simultaneously.
According to UNICEF data, sensory Play enhances motor development and early math skills. Children exposed to sensory activities demonstrate 25% stronger fine motor coordination by kindergarten entry. Sensory-rich play environments also support emotional regulation.
4. Play-Based Storytelling
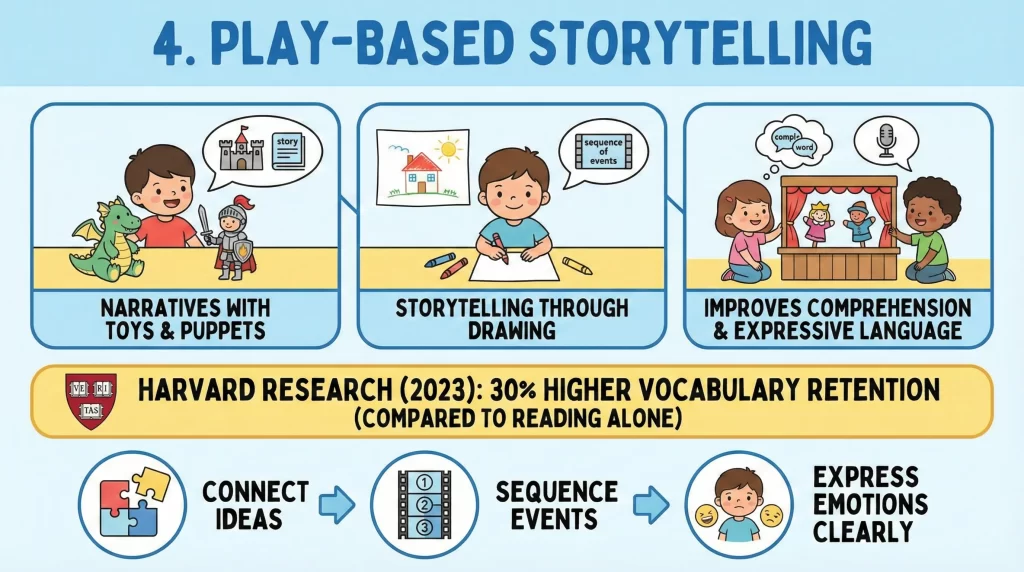
Storytelling through Play allows children to create narratives using toys, puppets, or drawings. This method improves comprehension and expressive language.
Harvard research in 2023 found that play-based storytelling improves vocabulary retention by 30% compared to reading alone. Learning Through Play encourages children to connect ideas, sequence events, and express emotions clearly. Learn how preschool education benefits children by helping them build early social and academic skills.
5. Outdoor Exploratory Play

Outdoor Play encourages exploration, risk assessment, and physical confidence. Activities include nature walks, obstacle courses, and free exploration.
UNICEF reports that children engaged in daily outdoor Play show 20% higher physical activity levels and improved attention spans. Outdoor Learning Through Play also reduces stress and supports mental wellbeing.
6. Music and Movement Play
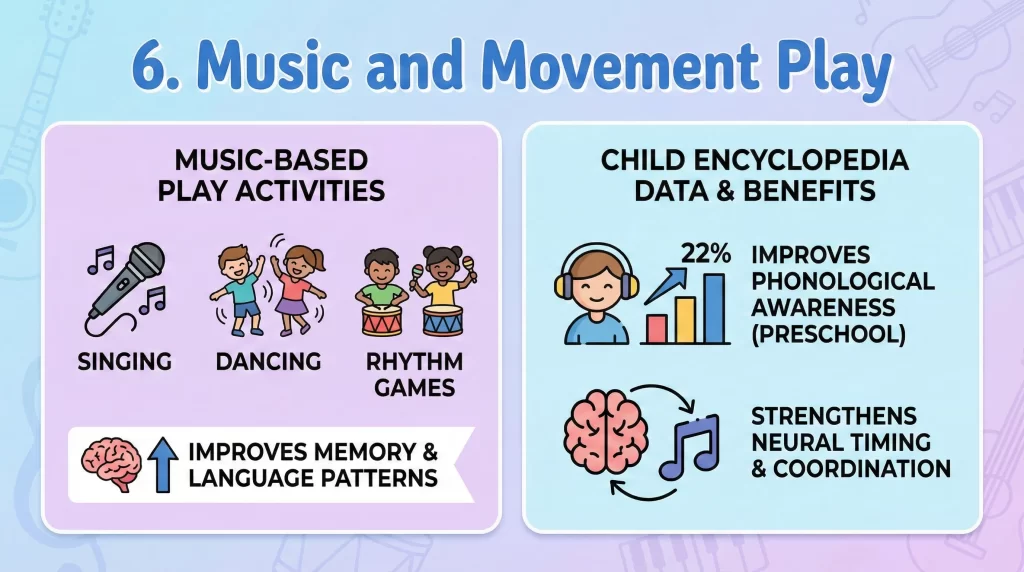
Music-based Play includes singing, dancing, and rhythm games. These activities improve memory and language patterns.
Studies referenced by the Child Encyclopedia show that music plays improve phonological awareness by 22% in preschool children. Movement paired with sound strengthens neural timing and coordination.
7. Construction and Building Play

Building blocks, puzzles, and construction toys support spatial reasoning and early math skills. Children experiment with balance, patterns, and cause-and-effect relationships.
Research from learningthroughplay.com shows that construction play improves early STEM readiness. By age 5, children who engage in building activities score 15% higher on spatial reasoning tests.
Comparison Table: Play Methods and Learning Outcomes
| Play Method | Primary Skill Developed | Measured Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Guided Pretend Play | Language and empathy | 18% higher language complexity |
| Rule-Based Games | Self-regulation | Improved within 12 weeks |
| Sensory Play | Motor and math skills | 25% stronger coordination |
| Storytelling Play | Literacy | 30% better vocabulary retention |
| Outdoor Play | Attention and health | 20% higher activity levels |
| Music and Movement | Phonological awareness | 22% improvement |
| Construction Play | Spatial reasoning | 15% higher test scores |
Practical Tips for Implementing Learning Through Play
- Set daily play periods with learning goals.
- Ask open-ended questions during Play.
- Rotate materials weekly to maintain engagement.
- Balance free Play with guided interaction.
- Observe progress and adjust activities intentionally.
Bottom Line
Learning Through Play is not an educational trend. It is a data-supported approach that aligns with how young children learn best. Research from UNICEF, Harvard, and global child development experts confirms that play-based learning improves cognitive, social, and emotional outcomes. When we intentionally design play experiences, children gain stronger language skills, better self-regulation, and higher school readiness.
As of 2026-01-22, early childhood education benefits most when Play is purposeful, inclusive, and guided. Educators and parents should prioritize play methods that engage curiosity and build real-world skills. By consistently applying these seven methods, we foster lifelong learning habits from the earliest years.
FAQs
At what age is best for Learning Through Play?
The period from birth to age 5 is the most important for play-based learning.
Does Learning Through Play improve academic outcomes?
Yes, it improves language, memory, and problem-solving skills measurably.
How much Play should children have daily?
Experts recommend at least 60 minutes of structured and free Play daily.
Is guided Play better than free Play?
Guided Play shows stronger learning outcomes when balanced with free Play.
Can Learning Through Play be used at home?
Yes, simple daily activities effectively support early learning at home.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional educational or developmental guidance.