Table of Contents
The Importance of Early Education shapes how children think, learn, and interact long before formal schooling begins. Research consistently shows that brain development is fastest between birth and age five. According to the Center on the Developing Child, over 90% of brain growth happens before age five. This makes early learning experiences critical, not optional. When children access quality early education, they build stronger cognitive, social, and emotional foundations.
In the United States, data from the National Institute for Early Education Research shows children who attend structured early education programs score higher in reading and math by third grade. They also show improved attention and self-regulation skills. Early education is not about pushing academics too early. It is about structured play, language exposure, emotional safety, and guided exploration.
This article explains the Importance of Early Education through six evidence-backed benefits. Each benefit connects early learning to long-term success using current data and clear takeaways. Parents, educators, and policymakers can use this guide to make informed decisions that support children from the very start.
1. Stronger Brain Development and Cognitive Growth
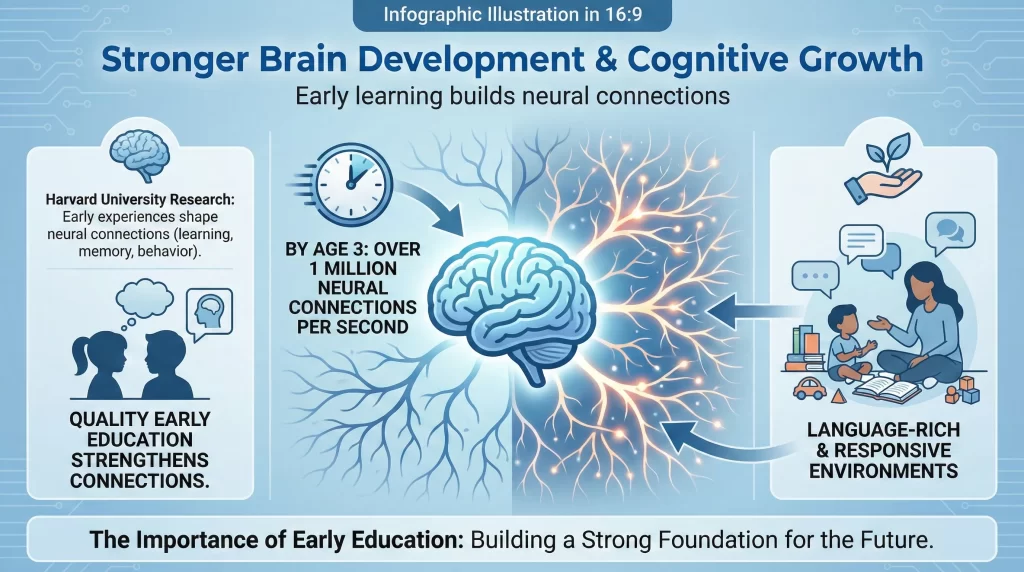
Early learning builds neural connections
The Importance of Early Education begins with brain architecture. Harvard University research confirms that early experiences shape neural connections that control learning, memory, and behaviour. By age three, a child’s brain forms over 1 million neural connections per second. Quality early education strengthens these connections through language-rich and responsive environments.
Children exposed to early learning programs show higher vocabulary scores by age five. The U.S. Department of Education reports a 31% improvement in early literacy skills among children attending structured preschool. These gains support smoother transitions into kindergarten and primary school. Preschool learning is one part of a child’s early growth. For a complete overview, explore our full
Early Childhood Education Guide covering learning methods, activities, and long-term benefits.
2. Improved Language and Communication Skills
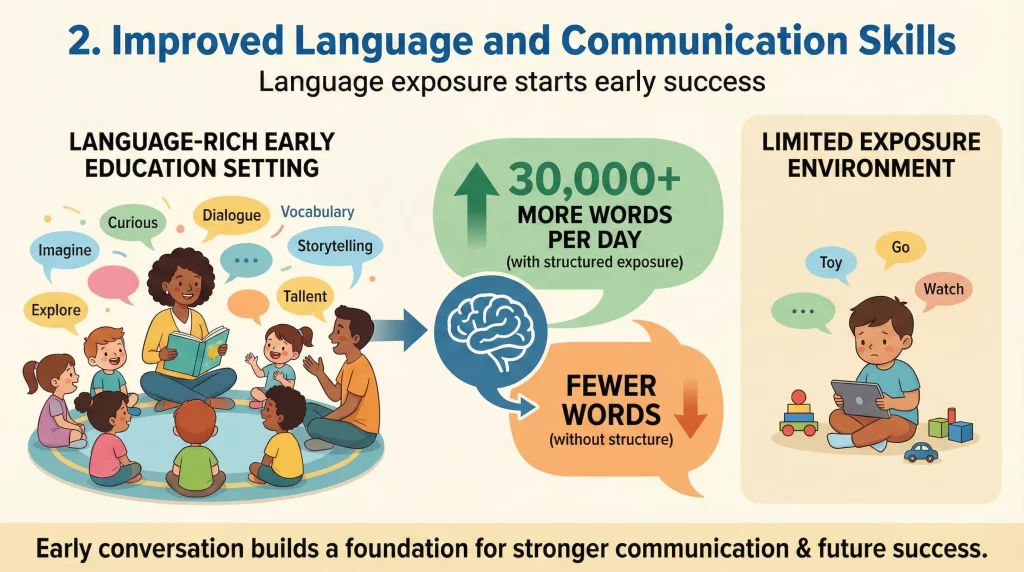
Language exposure starts early, and success
Language development is a core reason behind the Importance of Early Education. Children who hear more words and engage in conversation early develop stronger communication skills. Studies show that children in language-rich early education settings hear up to 30,000 more words per day than peers without structured exposure.
By age four, children in high-quality early programs demonstrate expressive language scores 40% higher than those in lower-quality programs. These skills directly support reading comprehension and classroom participation. Strong communication also reduces frustration-driven behaviour.
Here is a quick comparison showing language outcomes.
| Early Education Exposure | Vocabulary by Age 5 | Reading Readiness |
|---|---|---|
| Structured preschool | 1,200+ words | High |
| No formal early learning | Under 800 words | Moderate |
3. Better Social and Emotional Development

Learning emotions supports lifelong behaviour
The Importance of Early Education extends beyond academics into emotional intelligence. Early learning environments teach children how to share, manage emotions, and resolve conflicts. According to the American Psychological Association, children in early education programs show 25% fewer behavioural issues by age seven.
Social-emotional learning helps children understand empathy and cooperation. These skills predict long-term success more accurately than IQ alone. Children who develop emotional regulation early adapt better to classroom routines and peer relationships.
Educators report improved classroom behaviour and reduced anxiety among children with early education experience. These benefits persist into adolescence. Try simple early learning activities to support development at home.
4. Higher Academic Achievement Over Time
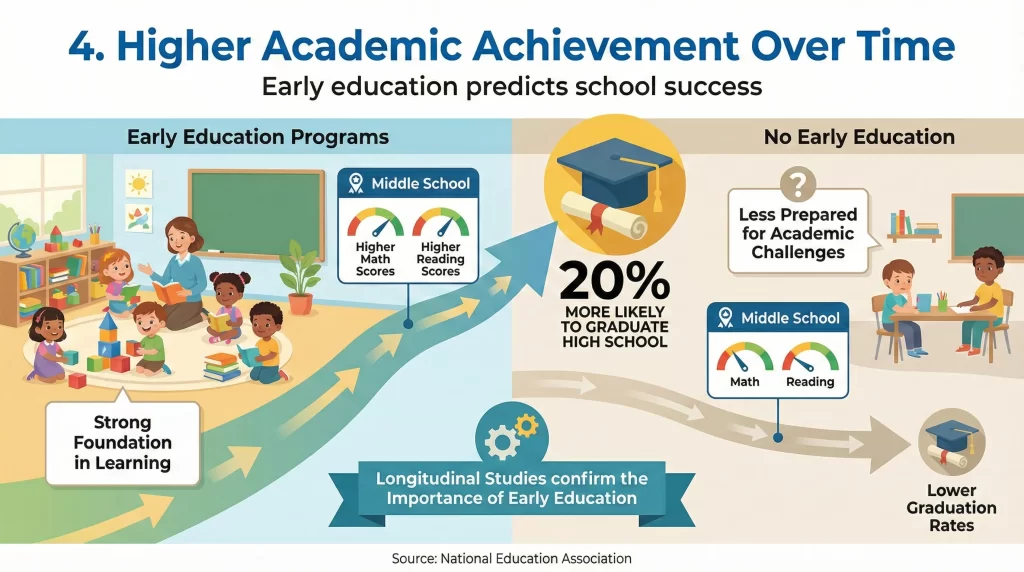
Early education predicts school success
Academic performance strongly reflects the Importance of Early Education. Longitudinal studies from the National Education Association show that children who attend early education programs are 20% more likely to graduate high school. They also show higher math and reading scores through middle school.
Early education builds pre-math skills like pattern recognition and counting. It also strengthens attention span and learning stamina. These skills compound over time, leading to consistent academic progress.
Key academic benefits include:
- Higher reading scores by grade three.
- Improved math proficiency by grade five.
- Reduced need for special education services.
5. Reduced Educational Gaps and Greater Equity
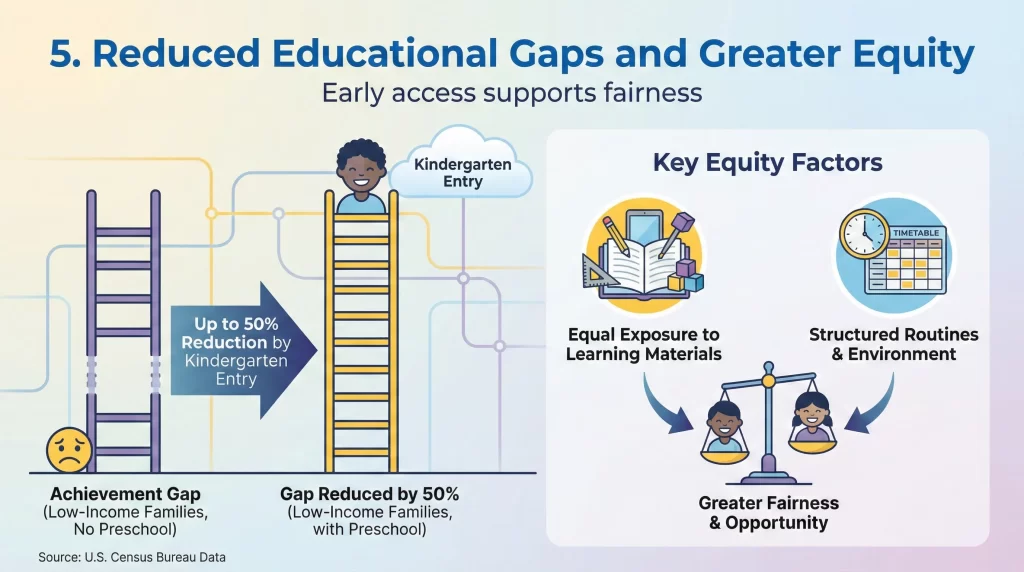
Early access supports fairness
The Importance of Early Education is especially clear in closing achievement gaps. Data from the U.S. Census Bureau shows that children from low-income families who attend preschool reduce learning gaps by up to 50% by kindergarten entry. Early education provides equal exposure to learning materials and structured routines.
Quality programs offer consistent support regardless of background. This reduces disparities linked to income, language, and access to resources. Children gain confidence and readiness alongside peers.
States investing in early education see long-term economic returns. Every $1 invested in early education yields up to $7 in societal benefits, according to the Heckman Equation. Discover why learning through play is one of the most effective teaching methods.
6. Long-Term Economic and Life Outcomes
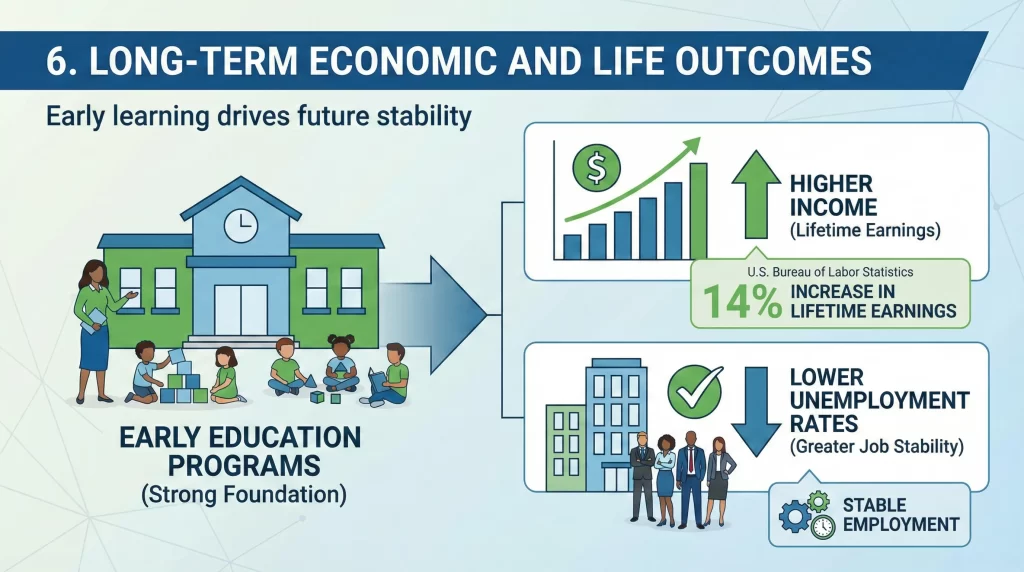
Early learning drives future stability
The Importance of Early Education extends into adulthood. Adults who attended early education programs earn higher incomes and experience lower unemployment rates. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics links early education participation to a 14% increase in lifetime earnings.
Early education also reduces crime rates and reliance on social services. These outcomes reflect stronger decision-making and social skills developed early.
Here are the key long-term impacts:
- Higher employment stability.
- Improved health outcomes.
- Greater civic engagement.
Bottom Line
The Importance of Early Education is supported by decades of research and current data. Early learning shapes brain development, language, emotional health, academic success, and long-term stability. These benefits do not fade with age. They compound over time and influence every stage of life.
Parents and educators should prioritize access to quality early education programs. Policymakers should continue investing in evidence-based early learning initiatives. Even small improvements in early education quality create measurable outcomes.
FAQs
Why is early education important before age five?
Brain development peaks before age five, making early learning critical for cognitive and emotional growth.
Does early education improve academic performance later?
Yes, it improves reading, math, and graduation rates through long-term skill development.
Is early education only about academics?
No, it focuses on social, emotional, and language development through guided play.
Can early education reduce learning gaps?
Yes, it significantly narrows gaps in income and access.
Are early education benefits long-lasting?
Yes, benefits extend into adulthood, including higher earnings and stability.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional educational or developmental guidance.