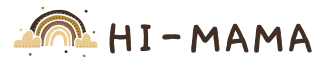Table of Contents
Learning Activities for Kids play a critical role in shaping cognitive, social, and emotional growth during early childhood. As of 2026-01-25, UNICEF reports that over 90% of brain development happens before age five, making structured learning through play essential during early years. When learning happens at home, children feel safe, confident, and more willing to explore new ideas.
Research from Education.com confirms that children engaged in daily learning activities at home show a 23% improvement in attention span and memory retention by age seven. These gains are strongest when activities are hands-on and age-appropriate. Families do not need expensive tools or complex lesson plans. Simple, intentional activities create meaningful learning moments when done consistently.
This guide focuses on Learning Activities for Kids that are fun, educational, and easy to manage at home. Each activity blends play with purpose and supports skill development across literacy, numeracy, creativity, and emotional intelligence. We aim to help parents make informed choices with clear benefits and real data.
1. Reading and Storytelling Activities
Why Reading Builds Strong Learning Foundations
Learning Activities for Kids that involve reading support language development and early literacy skills. According to Cambridge English, children who read aloud for 15 minutes daily improve vocabulary recognition by 35% within six months. Reading also strengthens listening skills and emotional understanding. Storytelling encourages imagination while teaching structure and sequencing.
Parents can rotate fiction, nonfiction, and picture books to maintain engagement. Asking children to predict story outcomes boosts comprehension and critical thinking. Reading together also increases emotional bonding and attention span. These moments help children associate learning with comfort and trust.
2. Math Through Everyday Play

Turning Numbers into Real-Life Skills
Learning Activities for Kids become more effective when math feels practical and relatable. Education.com reports that children exposed to hands-on math activities score 27% higher in problem-solving assessments by grade three. Counting toys, measuring ingredients, and sorting household items build number sense naturally.
Games involving patterns and comparisons improve logical reasoning. Simple activities like counting steps or comparing object sizes create learning without pressure. Math becomes less intimidating when children see its real-world value. Parents should use everyday language to explain numbers clearly.
3. Creative Art and Craft Projects
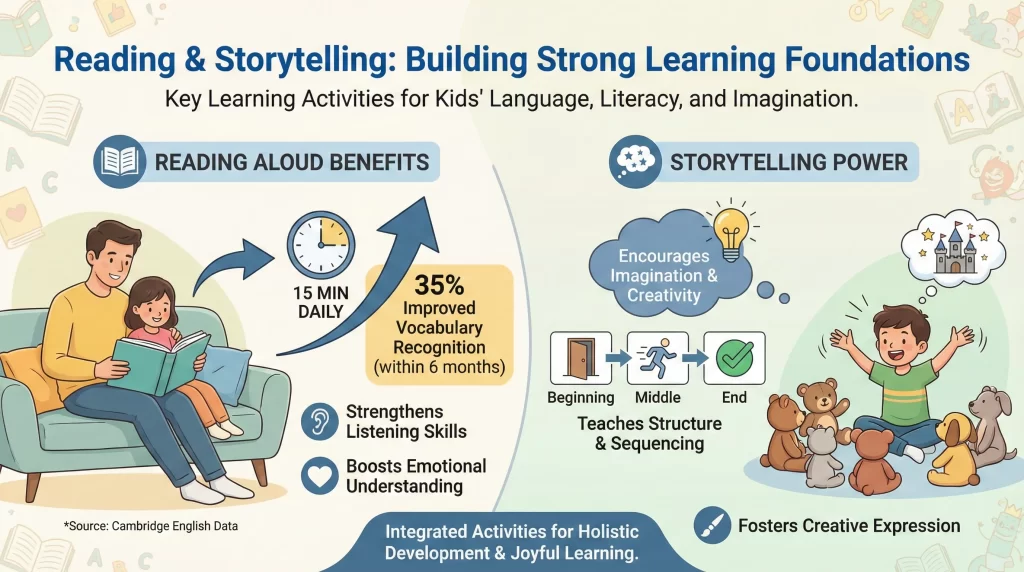
Supporting Emotional and Cognitive Growth
Creative Learning Activities for Kids improve fine motor skills and emotional expression. UNICEF data shows children involved in weekly art activities demonstrate 18% stronger emotional regulation by age eight. Drawing, painting, and crafting help children communicate ideas visually.
Art activities also support focus and patience. Using recyclable materials teaches sustainability awareness while encouraging creativity. Parents should allow freedom in outcomes rather than aiming for perfection. This approach builds confidence and self-expression.
4. Science Exploration at Home
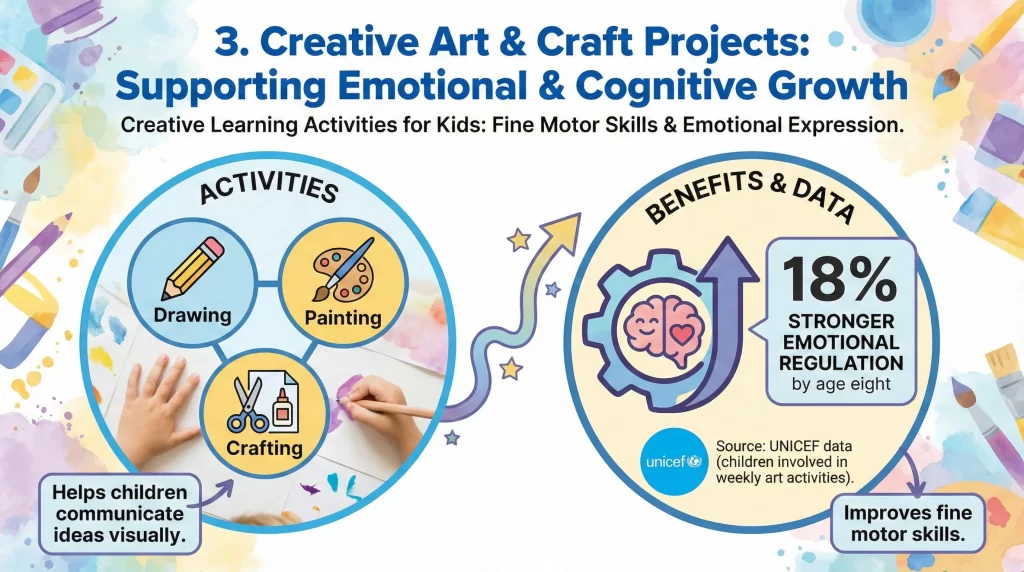
Encouraging Curiosity and Discovery
Learning Activities for Kids that include science spark curiosity and critical thinking. Simple experiments improve observation and reasoning skills. According to Fun Learning for Kids, children who explore basic science concepts weekly show a 21% increase in curiosity-driven questioning.
Activities like observing plant growth or mixing safe ingredients teach cause and effect. Parents should guide discussions using simple explanations. Science learning becomes meaningful when children see results firsthand.
5. Physical Movement and Learning Games
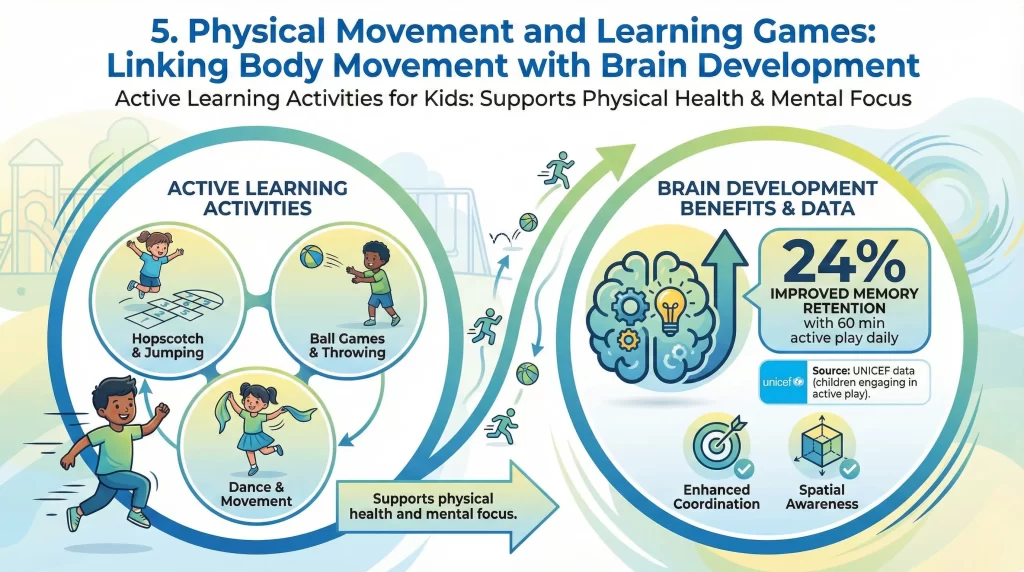
Linking Body Movement with Brain Development
Active Learning Activities for Kids support physical health and mental focus. UNICEF reports that children engaging in 60 minutes of active play daily show improved memory retention by 24%. Movement-based games enhance coordination and spatial awareness.
Activities like obstacle courses and action-based counting combine learning with exercise. Physical play also reduces stress and improves sleep quality. Parents should ensure activities remain fun and safe.
6. Music and Rhythm-Based Learning
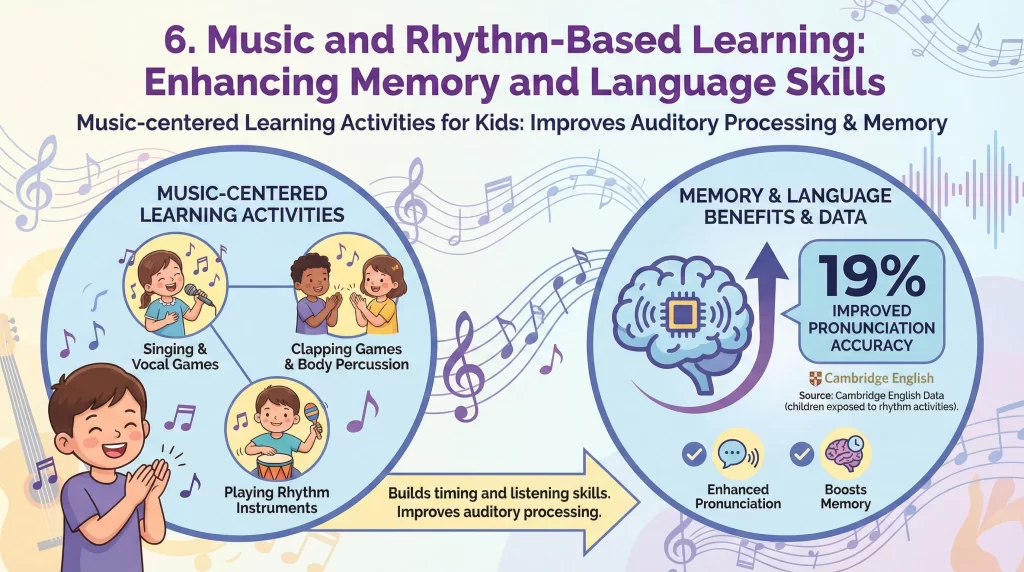
Enhancing Memory and Language Skills
Music-centered Learning Activities for Kids improve auditory processing and memory. Cambridge English notes that children exposed to rhythm activities improve pronunciation accuracy by 19%. Singing and clapping games build timing and listening skills.
Music also supports emotional expression and social bonding. Parents can introduce simple instruments or use household items creatively. Repetition reinforces learning through rhythm and sound.
7. Social Skills Through Role Play

Building Confidence and Communication
Learning Activities for Kids that involve role play support emotional intelligence and communication skills. Education.com data shows that role-playing improves empathy recognition by 22% in children aged five to nine. Pretend play allows children to explore real-life scenarios safely.
Activities like playing shop or family roles teach cooperation and problem-solving. Parents should encourage open-ended scenarios to foster creativity. These games also improve verbal expression.
8. Digital Learning with Purpose
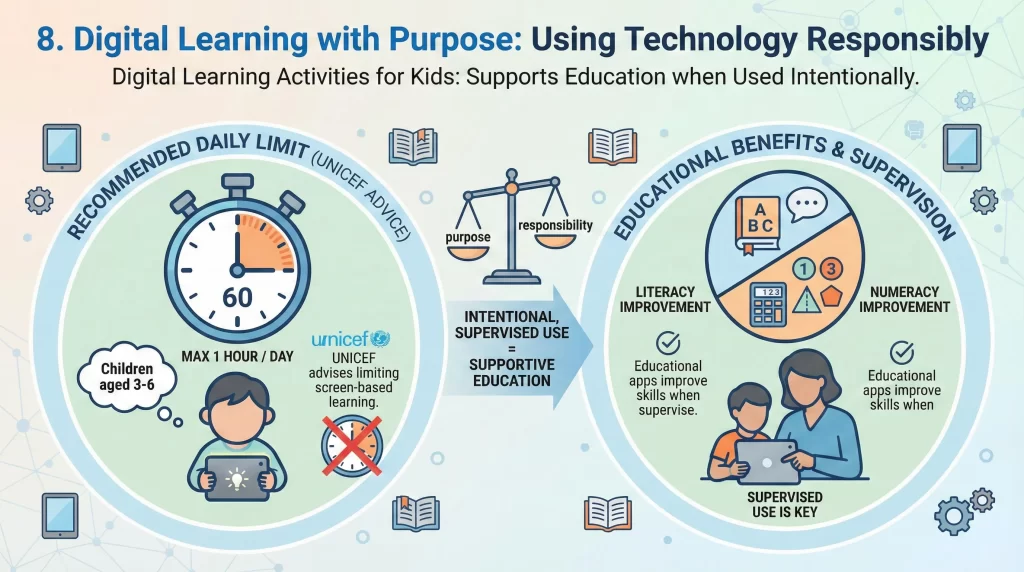
Using Technology Responsibly
Digital Learning Activities for Kids can support education when used intentionally. UNICEF advises limiting screen-based learning to one hour daily for children aged three to six. Educational apps improve literacy and numeracy when supervised.
Parents should choose platforms with interactive elements and clear learning goals. Screen time should complement hands-on learning rather than replace it. Balance ensures healthy development.
Learning Activities Comparison Table
| Activity Type | Skills Developed | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Reading | Literacy, focus | Daily |
| Math Play | Numeracy, logic | 4 times weekly |
| Art Projects | Creativity, motor skills | Weekly |
| Science Experiments | Curiosity, reasoning | Weekly |
| Physical Games | Coordination, memory | Daily |
| Music Activities | Language, rhythm | 3 times weekly |
| Role Play | Social skills | Weekly |
| Digital Learning | Literacy, numeracy | Limited daily |
Key Points to Remember
- Learning Activities for Kids work best when consistent and age-appropriate.
- Play-based learning improves retention and emotional engagement.
- Balance structured activities with free exploration.
- Parent involvement increases learning outcomes significantly.
Bottom Line
Learning Activities for Kids create meaningful learning experiences when designed with intention and balance. Data from 2026 confirms that children benefit most when learning combines play, structure, and emotional support. Parents do not need complex tools to support development. Simple activities, repeated consistently, deliver measurable improvements in focus, confidence, and skill mastery.
We recommend rotating activities weekly to maintain interest and reinforce learning outcomes. Combining physical, creative, and cognitive tasks ensures holistic growth. Children learn best when they feel safe, curious, and supported. By integrating these eight activities into daily routines, families can build strong educational foundations at home. Don’t miss our recent post about Learning Activities for Kids.
FAQs
What age group benefits most from these activities?
Children aged three to ten benefit most from structured learning activities at home.
How long should daily learning activities last?
Thirty to sixty minutes daily delivers optimal learning outcomes.
Are digital learning tools necessary?
No, hands-on activities provide equal or greater learning benefits.
Can learning activities replace school education?
No, they complement formal education effectively.
How often should activities change?
Rotating activities weekly maintains engagement and interest.
Disclaimer
This content is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional educational or developmental guidance for children.