- History of Cloud Computing
- Understanding Cloud Service Models
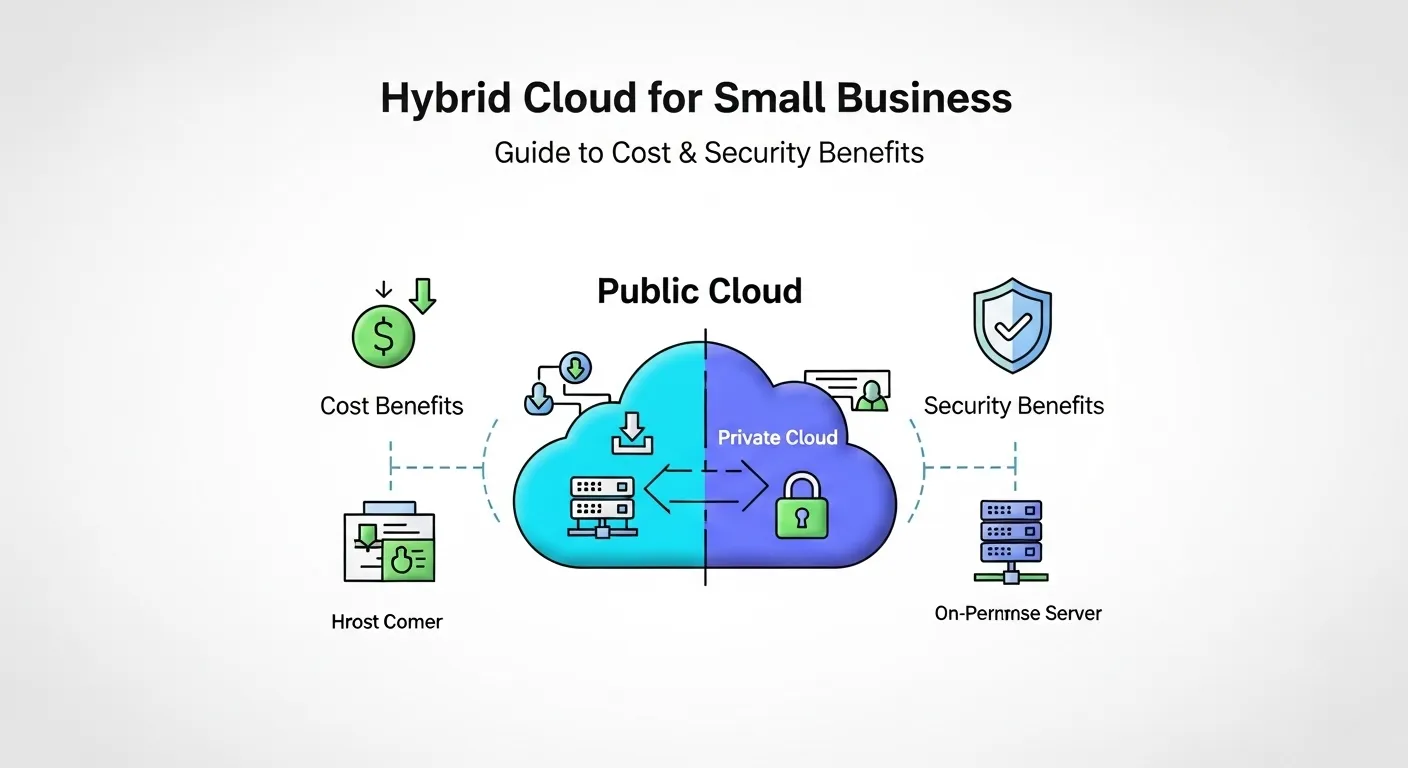
- Comparing Cloud Deployment Models
- Benefits of Hybrid Cloud for Small Businesses
- Common Challenges and Risks of Hybrid Cloud
- Security and Compliance in Hybrid Cloud Environments
- Cost Considerations and Pricing Models
- Tools and Platforms for Hybrid Cloud Management
- Real-World Use Cases and Industry Examples
- Best Practices for Small Business Adoption
- Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud Computing
- Final Thouhts
- FAQs
- References
- Author’s: Chang Russell
We often hear small businesses say they need to do more with less. Hybrid cloud computing for small business solutions make that possible by offering affordable access to big-company technology. They help a growing business compete without spending huge amounts on hardware or IT staff.
These businesses see the cloud not just as a trend but as a real way to store files, run applications, and secure customer data. In 2024, studies showed that 92% of companies already use cloud services, and small businesses are right in the middle of this movement.
History of Cloud Computing
I like to think of the cloud as an idea that’s been around longer than most of us realize. Back in the 1990s, engineers would draw internet networks as a “cloud” in diagrams. That’s where the name “cloud computing” first came from.
In the early 2000s, broadband internet and mobile devices made cloud technology practical. This was when services like online storage, backup, and hosting appeared. Today, businesses use advanced tools like AI, machine learning, and hybrid cloud systems to stay flexible and safe.
Understanding Cloud Service Models
We sometimes get lost in terms, but there are really three main service models. Let’s keep them simple.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
This means renting IT resources like servers and storage instead of buying them. Providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure let you pay only for what you use.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Here, developers can use cloud-based tools to build applications faster. Think of Google App Engine or Salesforce Lightning they give you a ready-made environment so you can focus on coding, not setup.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
This is the easiest to understand. We’re talking about apps like Microsoft Office 365, QuickBooks Online, or Google Workspace. You pay a subscription and use them through a browser no need to install or manage software.
Comparing Cloud Deployment Models
When small businesses shop for cloud solutions, they usually hear about three deployment types.
Public Cloud
A public cloud is shared by many users but managed by a provider. It’s affordable, elastic, and updated often. Dropbox and AWS are common examples.
Private Cloud
This one lives inside your company. It’s built on your own hardware, giving you more control and security. But it costs more to set up and maintain.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid model mixes the two. Sensitive data stays private, while other workloads go public. It’s like using the best of both worlds for security and cost savings.
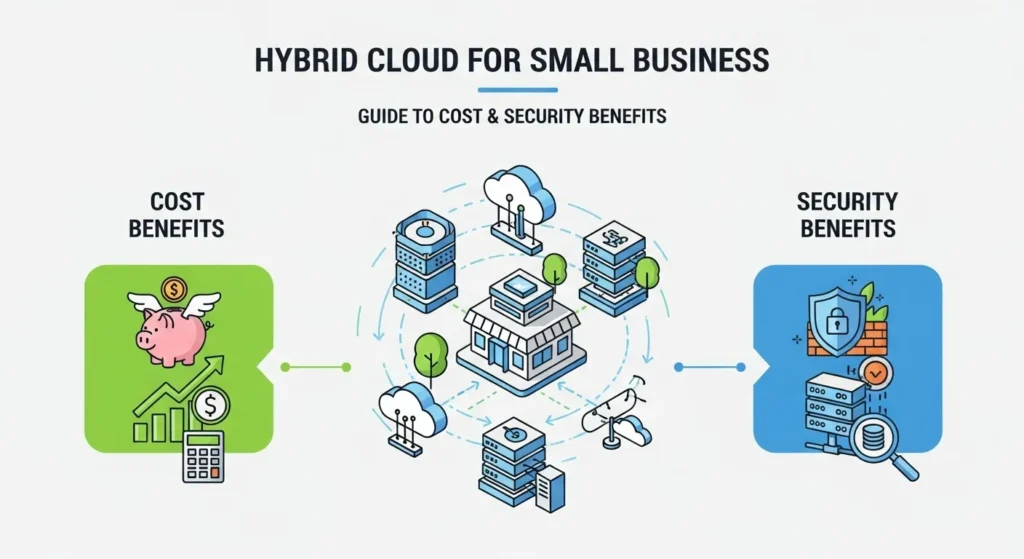
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud for Small Businesses
Small businesses love hybrid cloud because it’s practical. Here are some reasons:
- Flexibility: Keep sensitive files private while using public cloud for apps or extra storage.
- Cost savings: Pay only for what you use. No wasted money on idle hardware.
- Scalability: Scale up quickly during busy seasons like Black Friday. Retailers often need 1000 times more capacity during sales events.
- Disaster recovery: Use the 3-2-1 rule 3 copies of data, 2 media types, 1 offsite backup.
- Remote work support: Employees can securely log in from anywhere.
- Innovation: Access AI and machine learning tools for analytics and better decision-making.
Common Challenges and Risks of Hybrid Cloud
Of course, no solution is perfect. Here’s what small businesses struggle with:
- Reliance on internet speed and uptime.
- Security gaps if systems are not set up correctly.
- Compliance worries 74% of SMBs say this is their biggest challenge.
- Reduced visibility when part of the system is outside company walls.
- Training requirements for staff.
- Hidden costs like egress fees when moving data between clouds.
- Compatibility issues with older applications.
Security and Compliance in Hybrid Cloud Environments
They say security is a shared responsibility. Providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure offer strong defenses, but businesses must manage access and protect data. In 2024, reports showed that 37% of companies had API security incidents. That’s a warning sign.
Compliance is another headache. Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, small businesses must prove their data is protected. Hybrid systems help by keeping sensitive information private while still benefiting from public cloud features.
Cost Considerations and Pricing Models
We need to talk about money because that’s what most business owners care about.
- Dropbox offers free plans, but paid versions start at $15 per user per month.
- Carbonite backup services cost around $50 per month.
- AWS and Azure often provide free tiers, then shift to pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Traditional dedicated hosting is expensive; shared hosting is cheaper but less reliable. Cloud hosting balances cost and uptime.
RackConnect Global even guarantees 99.95% uptime, which is far better than most in-house servers.
Tools and Platforms for Hybrid Cloud Management
When running hybrid setups, businesses rely on tools for control and monitoring. Some popular ones are:
- Azure Stack and Azure Arc
- AWS Outposts and CloudWatch
- Google Anthos
- VMware Cloud Foundation
- Kubernetes and Docker
- Terraform and Ansible
These tools help businesses monitor usage, secure access, and optimize costs across private and public environments.
Real-World Use Cases and Industry Examples
We can see hybrid cloud in action across industries:
- S&P Global Ratings moved 100+ applications to AWS in one month.
- YBVR, a video streaming company, uses hybrid systems to livestream 360-degree events requiring massive bandwidth.
- Retail businesses handle peak demand with cloud bursting, ensuring sites don’t crash on busy shopping days.
- SMBs often modernize IT with hybrid cloud, upgrading connectivity and analytics for smoother operations.
Best Practices for Small Business Adoption
If you’re a small business considering hybrid cloud, here’s a checklist:
- Build a clear strategy decide what data goes where.
- Use encryption, multi-factor authentication, and zero-trust security.
- Track spending with budget alerts and monitoring tools.
- Always back up using the 3-2-1 rule.
- Train IT staff in cloud architecture and automation.
- Test disaster recovery plans regularly.
- Classify data by sensitivity and create migration steps.
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud Computing
Looking ahead, we see even more growth. By 2025, SMBs will adopt more customized services for flexibility and security. The market is forecasted to reach £275.5 billion by 2029, growing at 22.12% CAGR.
By the end of 2024, 90% of enterprises are expected to use hybrid management systems. The future is about automation, stronger compliance tools, and tighter integration between public and private platforms.
Final Thouhts
We can say hybrid cloud is no longer just an option it’s becoming the standard. It allows small businesses to stay secure, save costs, and scale when needed. With real-world examples, strong tools, and proven best practices, the benefits are hard to ignore.
As technology moves forward, hybrid cloud computing for small business solutions will keep evolving. Small businesses that embrace this path today position themselves for long-term success tomorrow.
FAQs
What is hybrid cloud computing?
It’s a mix of private and public clouds that lets businesses store sensitive data securely while using public cloud for scalability and cost savings.
Why should small businesses use hybrid cloud?
It offers flexibility, lower costs, stronger security, and the ability to scale quickly during busy times like holiday sales.
Is hybrid cloud expensive?
Not always. Many services use pay-as-you-go pricing, so you only pay for what you need. It can be cheaper than owning all hardware.
How does hybrid cloud help with compliance?
Sensitive data can stay in a private cloud to meet regulations, while public cloud supports less regulated workloads.
References
- Foundry. (2024). Cloud Computing Research Report.
- Flexera. (2024). State of the Cloud Report.
- Fortinet. (2024). Cloud Security Report.
- Salt Security. (2023–2024). State of API Security Reports.
- S&P Global Ratings. (2022). Migration Case Study with VMware Cloud on AWS.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS). Official Documentation & Pricing.
- Microsoft Azure. Products and Services Overview.
- IBM Cloud. Services and Solutions.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Global Regions and Services.
- RackConnect Global. Service Uptime Guarantees.
- Carbonite. Cloud Backup and Recovery Pricing.
- Dropbox. Business Plans and Pricing.
- YBVR. (2023). 360° Video Streaming Case Study.
- Gartner. (2024). Hybrid Cloud Market Forecast.
- Jon Heimerl. Insights from Four Decades in Information Security.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Small businesses should consult IT and legal experts before making decisions about cloud services, security, or compliance.
Author’s: Chang Russell
With years of experience guiding small and medium businesses through digital transformation, I believe hybrid cloud is the bridge between affordability and security. My focus is helping SMBs grow smarter with the right mix of technology.