Introduction to TIG Welding
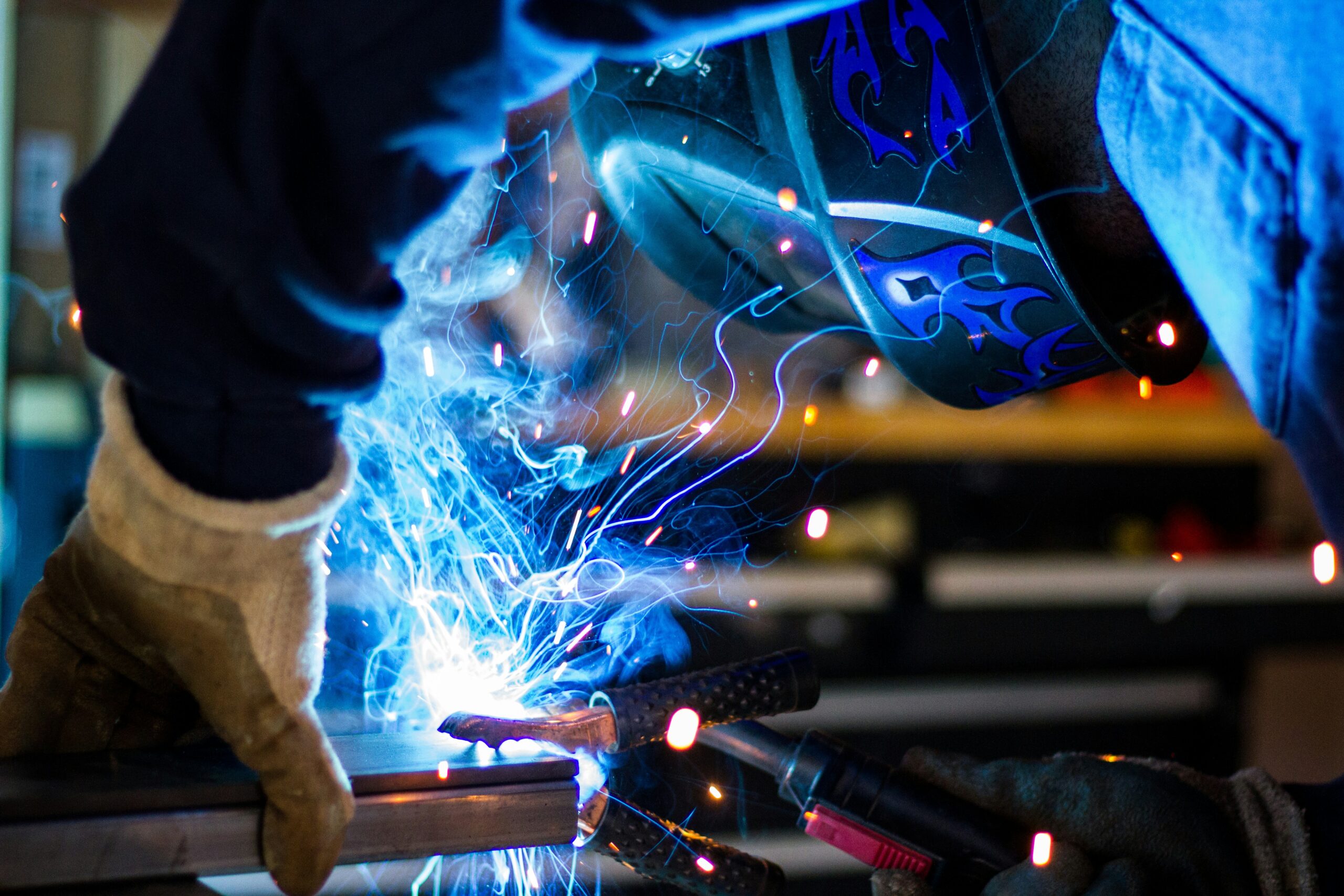
Tungsten Inert Gas welding, widely recognized as TIG welding, is a skill that commands respect in both industrial sectors and artistic fields. This technique stands out because it produces high-quality joins with remarkable precision and control. Whether crafting complex metal art pieces or working on high-grade industrial projects, understanding TIG welding can transform your work. Let’s explore the vastly engaging world of TIG welding and how mastering its techniques can lead to impeccable results.
Essential TIG Welding Techniques
To become proficient in TIG welding, it’s crucial to grasp and practice several techniques that foster steadiness and care. Maintaining a consistent arc length and evenly feeding the filler material distinguish amateur welds from expert ones. These techniques require a welder to develop a steady hand and a watchful eye. Beginners are encouraged to practice various materials to perfect their craft. Knowledge from a comprehensive guide can considerably bolster your understanding and application of these techniques, providing you with a solid foundation and confidence in your welding endeavors.
Choosing the Right Materials
In TIG welding, the materials you choose can make all the difference. Aluminum, with its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, is excellent for projects needing durability without the extra weight. However, aluminum can be prone to contamination if not adequately prepped. Meanwhile, stainless steel offers excellent strength but requires careful heat management to prevent warping and distortion. Knowing the inherent qualities of metals and how they interact with welding techniques is vital to achieving seamless results.
The Role of Equipment in Precision Welding
Precision in TIG welding is heavily dependent on the equipment used. The welding machine must be capable of adjusting the amperage to accommodate various thicknesses and types of metals. Carefully selecting tungsten electrodes suited to the specific materials is critical, as these choices affect the arc’s stability and the weld’s strength. Moreover, using inert gases like argon effectively eliminates contamination risks, ensuring a clean and robust weld. Assembling a toolkit customized to the specific demands of each project can significantly influence the success of the welding task, making the welding experience both efficient and gratifying.
Also Read: The Role of Braille Signs in Enhancing Accessibility
Safety First: Practices for a Secure Workspace
Safety is paramount in any welding process, and TIG welding is no exception. Ensuring the workspace is ventilated correctly protects against the toxic fumes often released during welding. Donning the appropriate protective gear, such as gloves, helmets equipped with auto-darkening filters, and flame-resistant clothing, is essential to safeguard against immediate and long-term hazards. Additionally, maintaining an organized and clutter-free workspace helps prevent accidents and contributes to smoother workflow operations. By adhering to these safety practices, welders protect themselves and enhance their work’s quality and reliability. A secure environment fosters better focus and attention to detail.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
The journey to becoming an expert in TIG welding is perpetual. Embracing a continuous learning mindset is crucial to staying at the forefront of this craft. Welders should seek opportunities to expand their knowledge by participating in workshops, joining online communities, and staying informed about industry advancements. As welding technology and techniques evolve, remaining adaptable and open to new ideas is essential for growth and success. By engaging with the community and taking advantage of educational resources, welders can refine their skills, foster innovation, and maintain a competitive edge.